Perennial flowers are a beautiful addition to any garden, providing vibrant colors and blooms year after year. However, as they grow and spread, you may find the need to divide and transplant them to maintain their health and vigor. In this guide, we will discuss the process of dividing and transplanting perennial flowers to help you successfully manage and propagate your garden favorites.
Why Divide Perennial Flowers?
Over time, perennial flowers can become overcrowded, leading to reduced blooming, smaller flowers, and overall decline in plant health. Dividing them allows you to rejuvenate the plants, promote better growth, and create new plants to expand your garden or share with others. Additionally, dividing perennials helps prevent them from outgrowing their space and competing for nutrients.

When to Divide Perennial Flowers
The best time to divide most perennial flowers is in early spring or fall when the weather is cool and plants are not actively blooming. This timing allows the plants to establish their roots in the new location before the stress of summer heat or winter cold sets in. However, some perennials may have specific preferences, so it’s essential to research the particular plant species you are working with.
How to Divide Perennial Flowers
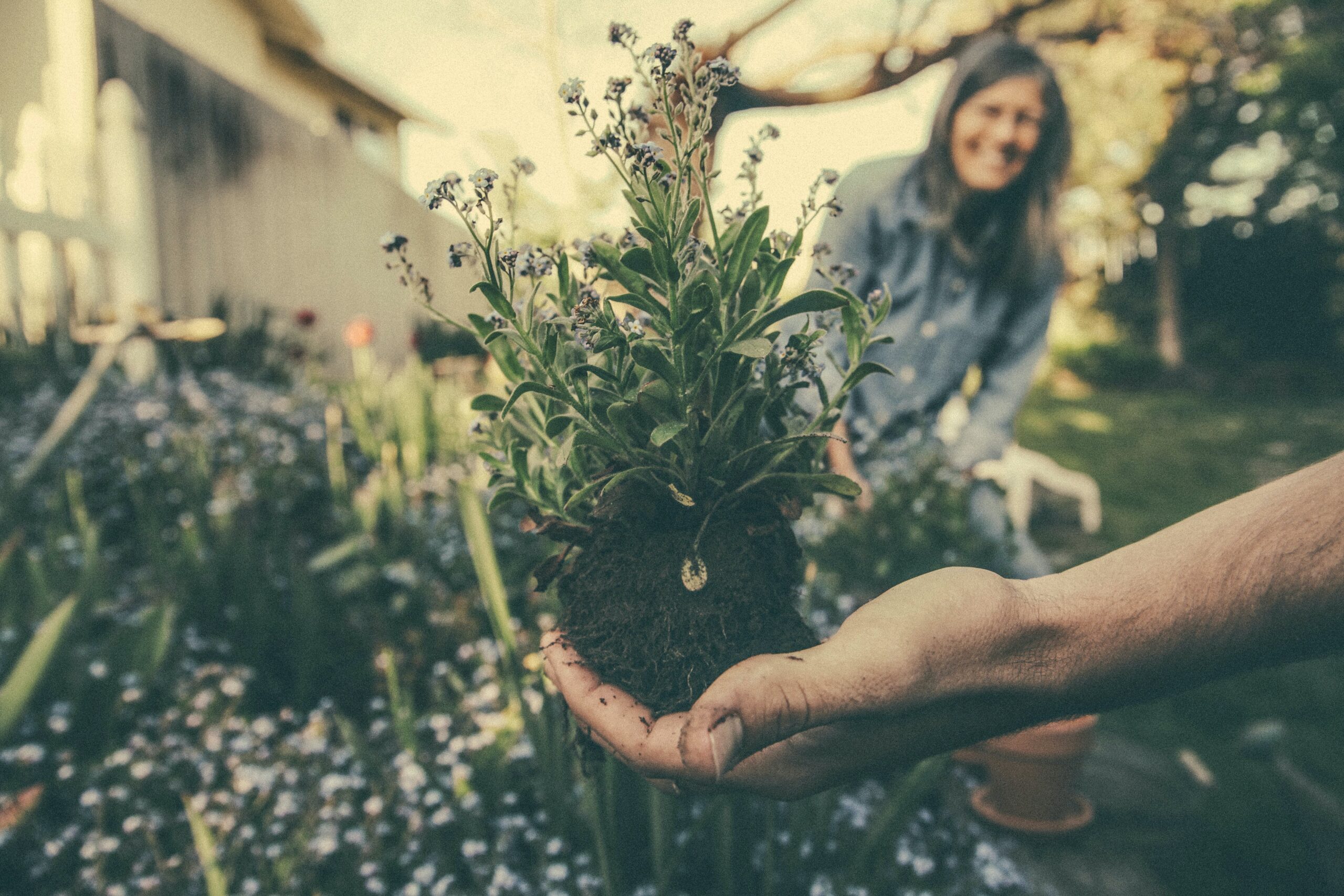
1. **Prepare the Plant**: Water the plant thoroughly a day or two before dividing to ensure the soil is moist and easier to work with. Dig around the plant, loosening the soil to expose the root ball.
2. **Divide the Plant**: Use a sharp shovel, garden fork, or knife to divide the plant into sections. Make sure each division has healthy roots and shoots. Some plants can be gently pulled apart by hand.
3. **Replanting**: Dig a hole in the new location, amend the soil with compost if needed, and place the divided plant at the same depth as it was previously growing. Water the plant well after transplanting to help it settle in.

Transplanting Tips
– **Watering**: Keep the transplanted perennial well-watered in the weeks following transplanting to help it establish in its new location.
– **Mulching**: Apply a layer of mulch around the base of the plant to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
– **Fertilizing**: Avoid fertilizing newly transplanted perennials immediately; wait until they show signs of new growth.

Common Perennials to Divide
Some popular perennial flowers that benefit from division include hostas, daylilies, irises, peonies, and asters. These plants tend to become overcrowded over time, leading to decreased flowering and overall performance.

Conclusion
Dividing and transplanting perennial flowers is a rewarding task that can help rejuvenate your garden and create new plantings to enjoy. By following the proper techniques and timing, you can ensure the health and vitality of your perennial flowers for years to come. Remember to research the specific requirements of each plant species and enjoy the process of propagating and expanding your garden with beautiful blooms.

Leave a Reply